Boils: Causes, Symptoms, and Natural Remedies
Boils, medically referred to as furuncles, are painful swellings on the skin caused by infections of sweat glands or hair follicles. They commonly occur during the summer months and can appear anywhere on the body, with a preference for areas prone to friction, such as the face, neck, and buttocks.
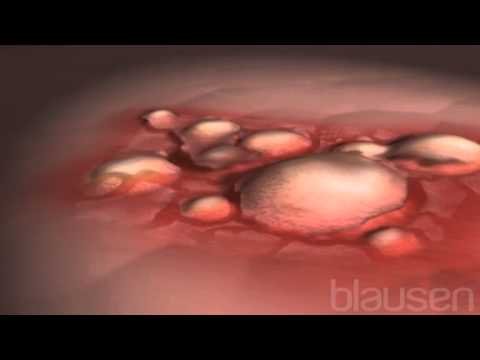
Causes of Boils
Boils are primarily caused by staphylococcus germs that enter the skin through cuts, pimples, or hair follicles. Factors such as poor hygiene, weakened immune system, and a toxic bloodstream due to an unhealthy diet contribute to their development.
Symptoms and Progression
The initial stage of a boil is marked by the appearance of a red, tender nodule on the skin, which gradually increases in size and fills with pus. Multiple boils may develop in the same area or different parts of the body, leading to discomfort, itching, and sometimes fever.
Symptoms of Boils on the Buttocks
Boils typically start as red, tender, and painful bumps on the skin. Over time, they fill with pus, becoming softer and more prominent. These bumps may eventually rupture, leading to pus discharge. Other symptoms include red or purple discoloration, swelling, and the development of a crust over unruptured boils.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of boils on the buttocks is bacterial infection, commonly by Staphylococcus aureus. Factors contributing to their development include skin folds, hair, sweat, friction, and certain medical conditions like diabetes, eczema, or immune system disorders. Additionally, smoking and small skin injuries increase susceptibility to boils.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing boils involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional. Treatment options include:
- Home Remedies: Warm compress application, maintaining a balanced diet, and natural home treatments.
- Oral and Topical Medications: Antibiotics, antiseptics, antibacterial soap, and hand sanitizer.
- Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding picking at the boil, maintaining hygiene, washing clothes separately, bathing regularly, and managing weight to reduce skin folds.
- Medical Procedures: Incision and drainage (lancing) by a healthcare provider, and packing the incision with gauze.
Complications and Prevention
Complications from boils can arise if the infection spreads, leading to severe scarring, carbuncles, cellulitis, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, or sepsis. Preventive measures include avoiding close skin contact with infected individuals, maintaining hand hygiene, bathing regularly, washing personal items, and protecting open wounds.
Outlook
Most boils on the buttocks can be effectively managed with supportive home therapies. However, larger or persistent boils may necessitate medical intervention. While boils themselves are usually not life-threatening, complications can occur, emphasizing the importance of seeking medical attention for severe or recurring cases.
Bottom Line
Boils on the buttocks, though discomforting, are manageable skin infections that require proper care and attention. Understanding their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures empowers individuals to effectively address and prevent these common conditions, promoting overall skin health and well-being.
Treatment Approaches
Effective treatment of boils begins with cleansing the system and adopting a nutritious diet. A diet rich in fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports the body’s natural healing process. Warm-water enemas and dietary restrictions, such as avoiding sugary foods and beverages, are recommended to detoxify the body.
Home Remedies for Boils
Several home remedies can provide relief from boils and promote faster healing. Garlic and onion poultices applied externally help ripen boils and facilitate drainage. Bitter gourd juice, when consumed daily on an empty stomach, detoxifies the body and reduces inflammation.
Preventive Measures
Maintaining good personal hygiene, including regular bathing and washing of clothes and bedding, is essential for preventing boil infections. Avoiding sharing personal items and keeping cuts and wounds clean can also reduce the risk of boils.
Conclusion
Boils are a common skin condition caused by bacterial infections, often exacerbated by poor hygiene and dietary habits. By adopting preventive measures, such as maintaining cleanliness and following a healthy lifestyle, individuals can minimize the risk of boil development and promote overall skin health.

FAQS
- What are the main causes of boils? Boils are primarily caused by bacterial infections, particularly staphylococcus germs, which enter the skin through cuts, pimples, or hair follicles.
- How can I prevent the recurrence of boils? Practicing good personal hygiene, avoiding sharing personal items, and maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle can help prevent the recurrence of boils.
- Are boils contagious? Yes, boils can be contagious, especially if the bacteria responsible for their formation are present on the skin or in infected areas.
- Can dietary changes help in managing boils? Yes, adopting a nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and avoiding sugary and processed foods can support the body’s immune system and aid in managing boils.
- When should I seek medical attention for boils? If a boil is large, painful, or accompanied by fever, or if it does not improve with home remedies, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.
