Introduction to Asthma
Everything You Need to Know About Asthma: Symptoms, Types, Causes, Prevention, and More
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the airways to the lungs, making breathing difficult and sometimes even dangerous. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the various aspects of asthma, including its symptoms, causes, types, diagnosis, treatment options, exacerbations, prevention strategies, and when to seek medical assistance.
Asthma, derived from the Greek word for “panting and short-drawn breath,” is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by chest tightness, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. This article explores the symptoms, causes, and holistic approaches to managing asthma.
Symptoms of Asthma
Asthma manifests through a range of symptoms, with wheezing being the most common. Other symptoms may include coughing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, difficulty speaking, anxiety, fatigue, and more. While these symptoms can vary from person to person, it’s essential to recognize when they occur and seek medical advice if they persist or worsen. Asthma patients experience recurring episodes of wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. These symptoms often worsen at night or during sleep, leading to restlessness and fatigue. Severe asthma attacks may cause increased heart rate, profuse sweating, and abdominal pain.
Causes of Asthma
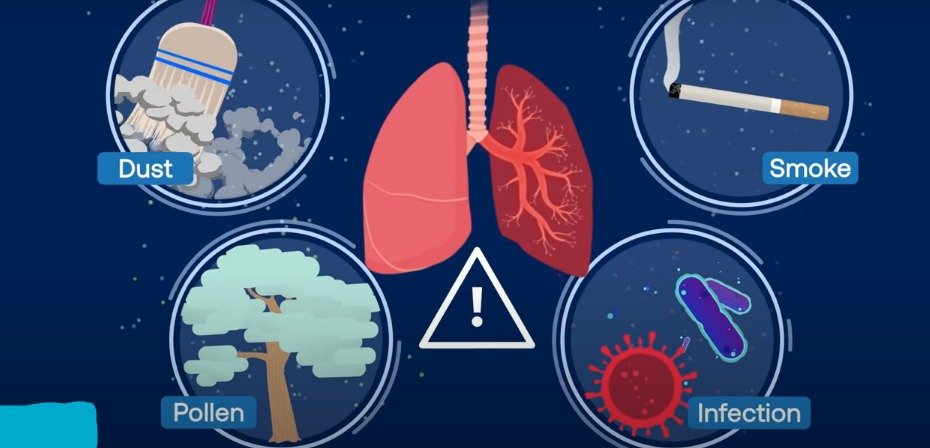
The exact cause of asthma remains unknown, but several factors contribute to its development. Genetics, viral infections during childhood, and the hygiene hypothesis are among the potential triggers. Additionally, various environmental factors such as allergens, irritants, intense emotions, weather conditions, and certain medications can exacerbate asthma symptoms.Asthma can be triggered by various factors, including allergens such as dust, pollen, and animal dander. Allergic reactions and bronchial constriction contribute to asthma symptoms. Emotional tension, air pollution, infections, and hereditary factors also play a role in asthma development.
Types of Asthma
Asthma is not a one-size-fits-all condition; it comes in various forms. Allergic asthma, non-allergic asthma, occupational asthma, exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, aspirin-induced asthma, nocturnal asthma, and cough-variant asthma are some of the different types, each characterized by distinct triggers and symptoms.

Treatment Approaches
Diagnosing asthma involves a combination of health history assessments, physical examinations, and breathing tests. Treatment strategies aim to manage symptoms and prevent exacerbations. Quick-relief medications, long-term control medications, and biologics are among the treatment options prescribed based on the severity and type of asthma. While modern medical treatments provide symptomatic relief, they do not offer a cure for asthma. Natural remedies and holistic approaches focus on strengthening the body’s immune system and reducing inflammation. Dietary modifications and lifestyle adjustments are essential for long-term asthma management.
Exacerbations and Prevention
Asthma exacerbations, commonly known as asthma attacks, occur when symptoms worsen due to airway inflammation and constriction. Prevention strategies focus on avoiding triggers, reducing allergen exposure, receiving allergy shots, taking preventive medications, and adopting a healthy lifestyle encompassing diet, weight management, smoking cessation, regular exercise, and stress management.
When to Seek Medical Assistance
It’s crucial to recognize the signs of worsening asthma symptoms and know when to seek medical assistance. Symptoms such as severe trouble breathing, confusion, blue lips or fingernails, and difficulty performing daily activities warrant immediate medical attention. Regular follow-ups with healthcare professionals help monitor asthma control and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Exercise-Induced Asthma: Symptoms, Treatment, and Safety Tips
Exercise-induced asthma, also known as exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB), can be a challenge for those who love physical activity. In this article, we’ll explore what exercise-induced asthma is, its symptoms, risk factors, treatment options, and how to exercise safely with this condition.
Why Exercise Triggers Asthma
When engaging in physical activity, you breathe more air, but this air isn’t always adequately humidified and warmed, especially when breathing through the mouth. Dry, cool air entering the airways can irritate them, leading to constriction and inflammation, making breathing difficult.
Common Symptoms of Exercise-Induced Asthma
The symptoms of EIB usually include coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, and sometimes mucus production. These symptoms often occur within 5 to 20 minutes of starting exercise and may persist for about 30 minutes after stopping.
Risk Factors for Exercise-Induced Asthma
Several factors increase the risk of developing EIB, including a personal or family history of asthma, allergic rhinitis, exposure to air pollution or cigarette smoke, and engaging in certain sports or activities in cold, dry air.
Treatment Options for Exercise-Induced Asthma
Treatment for EIB typically involves using medications to manage symptoms and breathing exercises to improve lung function. Medications may include short-acting beta-agonists (SABAs), inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs), and anticholinergics.
Safety Tips for Exercising with Exercise-Induced Asthma
Despite having EIB, regular exercise is essential for overall health. To exercise safely, consider using your inhaler before working out, warming up and cooling down properly, covering your mouth with a mask or scarf in cold weather, and avoiding sports with continuous activity or cold air exposure.
When to Seek Medical Care
If you experience symptoms of EIB for the first time or if your existing symptoms worsen, it’s crucial to consult your doctor. Additionally, seek medical attention if you experience fainting, weakness, persistent coughing or wheezing, or any other concerning symptoms.
Summary
Exercise-induced asthma, or exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, occurs when physical activity triggers airway constriction and inflammation, leading to symptoms like coughing and wheezing. Despite the challenges, individuals with EIB can safely engage in exercise with proper management and precautions. By understanding the condition, following treatment plans, and exercising safely, individuals can maintain an active lifestyle while managing their asthma effectively. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.

Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations
Asthma patients benefit from alkaline-rich diets comprising fresh fruits, green vegetables, and sprouted grains. Avoiding acidic foods and allergens helps prevent asthma attacks. Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, adequate hydration, and stress management are also crucial for asthma management.
Home Remedies for Asthma
Natural remedies like honey, garlic, and turmeric offer relief from asthma symptoms. Honey acts as a natural expectorant, while garlic and turmeric possess anti-inflammatory properties. Mustard oil massages and steam inhalation with caraway seeds help alleviate congestion and improve breathing.
Yoga and Breathing Exercises
Yoga asanas and pranayamas strengthen the respiratory system and enhance lung capacity. Specific poses like sarvangasana and bhujangasana improve breathing, while pranayamas like kapalbhati and anuloma-viloma enhance lung function. Regular practice of yoga promotes overall well-being for asthma patients.

Other Natural Therapies
Additional natural therapies such as mud packs, steam baths, and enemas help detoxify the body and alleviate asthma symptoms. These therapies promote relaxation and reduce inflammation, contributing to improved respiratory health.
Conclusion
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that requires holistic management to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. By adopting natural remedies, dietary modifications, and lifestyle changes, asthma patients can reduce the frequency and severity of asthma attacks.
FAQS
- What are the main causes of asthma?
- Asthma can be triggered by allergens such as dust, pollen, and animal dander. Other factors include emotional stress, air pollution, infections, and genetic predisposition.
- How can asthma be treated naturally?
- Natural treatments for asthma include dietary modifications, herbal remedies, breathing exercises, and yoga. These approaches focus on reducing inflammation, strengthening the immune system, and improving lung function.
- Are there any dietary recommendations for asthma patients?
- Asthma patients should follow an alkaline-rich diet comprising fresh fruits, green vegetables, and sprouted grains. Avoiding acidic foods and allergens helps prevent asthma attacks.
- What role does yoga play in managing asthma?
- Yoga asanas and pranayamas strengthen the respiratory system, enhance lung capacity, and promote relaxation. Regular practice of yoga improves breathing and overall well-being for asthma patients.