Introduction to Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis, a painful joint condition associated with psoriasis, affects numerous individuals worldwide. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore various psoriatic arthritis medications, non-drug methods for pain relief, and natural alternatives to help manage this autoimmune condition effectively.
Understanding Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis arises when the immune system attacks not only the skin but also the joints, leading to inflammation and discomfort. While the pain primarily affects the fingers and toes, it can also manifest in other areas like the wrists, knees, ankles, neck, and lower back.
Untreated psoriatic arthritis can result in joint damage and loss of mobility. Seeking timely medical intervention, typically from a rheumatologist, is crucial for effective management.
Psoriatic Arthritis Medication for Pain Relief
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Common over-the-counter options like ibuprofen and naproxen can alleviate pain and reduce joint swelling. However, they may pose risks of gastrointestinal issues, heart problems, and kidney issues, especially with prolonged use or high dosages.
- PDE4 Inhibitors: Apremilast (Otezla) targets inflammatory processes and is prescribed for both psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Side effects may include gastrointestinal discomfort and weight loss.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): These medications, available in various forms, aim to slow or halt joint damage. While effective, they may suppress the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
- Biologic Drugs: Biologics like adalimumab and infliximab target specific immune pathways to reduce inflammation. They are typically prescribed when conventional DMARDs fail to provide relief. Biologics also carry risks of immune suppression and infusion-related reactions.
Nondrug Methods for Pain Management
- Topical Pain Relievers: Creams containing lidocaine or capsaicin can be applied directly to the skin for localized relief. However, they may cause skin irritation in some individuals.
- Steroid Injections: Corticosteroids injected into affected joints can provide targeted relief from inflammation. However, frequent injections may weaken tendons and ligaments over time.
- Nondrug Therapies: Various approaches such as acupuncture, physical activity, hot and cold therapy, dietary changes, light therapy, supports, meditation, and adequate rest can complement medication to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Customize Your Treatment
Finding the right combination of psoriatic arthritis medication and alternative therapies often involves a trial-and-error process. Collaborate closely with your healthcare provider to tailor a treatment plan that addresses your unique needs and preferences. Regular monitoring and adjustments may be necessary to optimize outcomes and enhance quality of life.
Empower yourself with knowledge about psoriatic arthritis and explore diverse treatment options to manage symptoms effectively and live well with this condition. Remember to prioritize self-care, seek support from healthcare professionals, and make informed decisions about your health journey.
Arthritis, derived from Greek words meaning “inflammation of joints,” is a chronic disease characterized by joint inflammation. This article explores the types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options for arthritis.
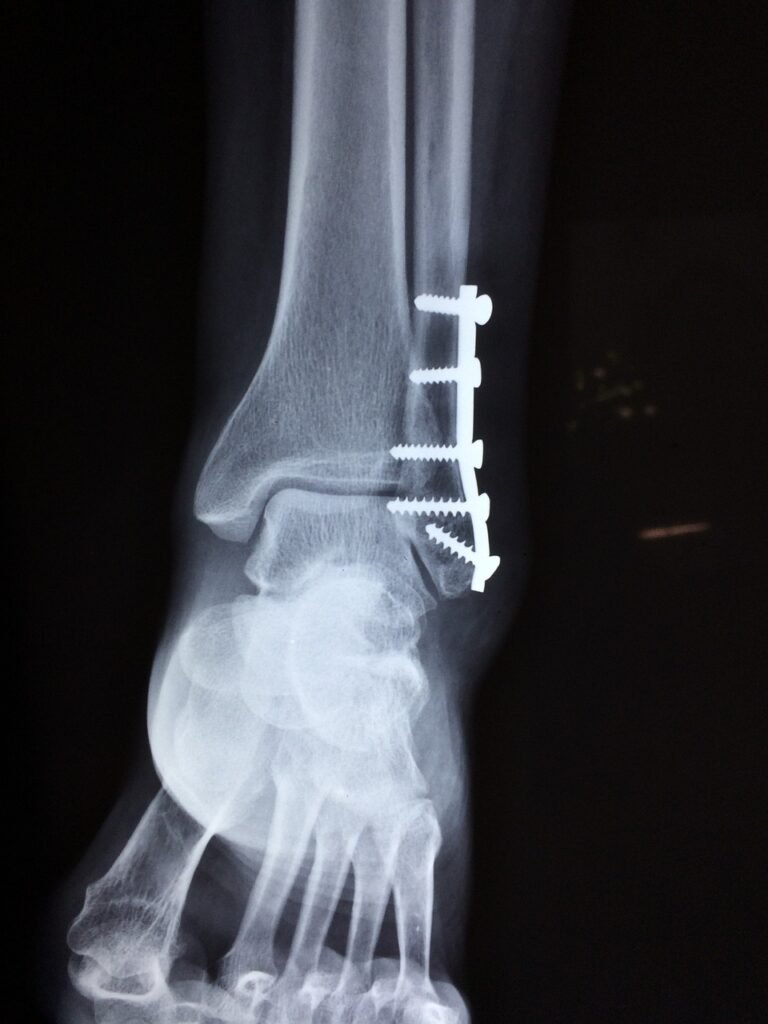
Understanding the Symptoms of Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by joint inflammation and other symptoms, PsA can significantly impact one’s quality of life if left untreated. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the various symptoms of PsA, providing valuable insights and practical tips for management.
1. Swelling
Swelling is a hallmark symptom of PsA, often presenting as a “sausage-like” swelling in the fingers and toes. This unique swelling can be extremely painful and may lead to permanent deformities if not addressed promptly.
2. Foot Pain
PsA commonly causes pain in the tendons of the feet, leading to conditions like plantar fasciitis and Achilles tendinitis. These conditions result in discomfort at the bottom of the foot and the heel, respectively.
3. Back Pain
Spondylitis, a secondary condition associated with PsA, leads to inflammation in the spine and pelvis. This inflammation can cause lower back pain, making it challenging to perform daily activities comfortably.
4. Morning Stiffness
Many individuals with PsA experience stiffness and inflexibility in the morning, particularly in the joints. This stiffness can persist for up to 45 minutes or longer, affecting mobility and flexibility.
5. Nail Problems
PsA can manifest as various nail abnormalities, including pitting, separation from the nail bed, discoloration, and crumbling. These changes can be early indicators of PsA and should not be ignored.
6. Red Skin Patches
The red, scaly rash commonly associated with psoriasis often precedes joint symptoms in individuals with PsA. Identifying these skin changes early can aid in the prompt diagnosis and management of PsA.
7. Fatigue
Chronic pain and inflammation in PsA can contribute to feelings of fatigue and exhaustion. Managing fatigue is essential for maintaining overall well-being and quality of life.
8. Reduced Movement
Stiffness, pain, and swelling in the joints and tendons can lead to reduced range of motion and mobility. Engaging in regular exercise and physical therapy can help improve flexibility and joint function.
9. Eye Pain
Eye inflammation is a common complication of PsA, affecting around 30 percent of individuals with the condition. Prompt evaluation and treatment by an eye care professional are crucial for preventing vision complications.
10. Anemia
Anemia, characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells, is often observed in people with PsA. Monitoring for signs of anemia, such as fatigue and paleness, is essential for comprehensive disease management.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above or suspect you may have PsA, it’s vital to consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early diagnosis and intervention can help prevent permanent joint damage and improve long-term outcomes
Inflammation is the hallmark of arthritis, triggered by joint tissue damage or injury. Symptoms include pain, stiffness, swelling, and deformity. Osteoarthritis is linked to structural changes in joint cartilage, while rheumatoid arthritis involves an inflammatory process of the synovium.
Treatment Options for Moderate to Severe Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a challenging condition characterized by joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, often accompanying psoriasis. Managing PsA effectively requires a multifaceted approach, including medications, surgical interventions, lifestyle modifications, and complementary therapies. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore various treatment options aimed at alleviating symptoms and preventing joint damage in individuals with moderate to severe PsA.
Medications for Psoriatic Arthritis
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen and prescription options such as celecoxib help reduce pain and inflammation associated with PsA. However, they may cause digestive issues as side effects.
- Traditional Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Drugs like methotrexate and sulfasalazine work by suppressing inflammation and slowing joint damage progression. They may have adverse effects on the lungs and kidneys and require careful monitoring.
- Biologics: Biologic DMARDs, including TNF-alpha inhibitors like adalimumab and IL-17 inhibitors like ixekizumab, target specific components of the immune system to manage inflammation and joint symptoms. Biologics are typically administered via injections or infusions and may increase susceptibility to infections.
- Enzyme Inhibitors: Newer medications like tofacitinib and apremilast inhibit enzymes involved in the immune response, offering oral alternatives to biologic therapies. Side effects may include headache, nausea, and upper respiratory infections.
- Oral Steroids: Short-term use of oral steroids like prednisone can provide temporary relief from PsA symptoms, but long-term use carries the risk of significant side effects.
Surgical and Other Treatments
- Joint Replacement Surgery: Severe joint damage may necessitate joint replacement surgery, where prosthetic implants replace damaged joints to restore function and alleviate pain.
- Steroid Injections: Localized pain and inflammation in specific joints can be managed with steroid injections, providing relief for weeks to months.
- Light Therapy: Ultraviolet (UV) light therapy, including UVB and PUVA, can reduce inflammation associated with PsA and psoriasis, promoting skin and joint health.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture: Stimulating specific points on the body with thin needles may help alleviate pain and improve overall well-being in some individuals with PsA.
- Massage: Manipulating soft tissues through massage therapy can provide relief from pain and stiffness, although scientific evidence supporting its efficacy for PsA is limited.
- Curcumin: The anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin, found in turmeric, may offer symptomatic relief for PsA, but further research is needed to establish its effectiveness.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: Mind-body practices like yoga and tai chi improve flexibility, reduce stress, and promote relaxation, benefiting individuals with PsA.
Lifestyle Changes
- Joint Protection: Implementing strategies to protect joints, such as using heat or cold treatments and avoiding overexertion, can minimize pain and prevent further damage.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins supports overall health and may help manage PsA symptoms.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity improves joint mobility, muscle strength, and overall fitness, contributing to better PsA management.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is crucial for individuals with PsA, as smoking can worsen symptoms and reduce treatment effectiveness.
Clinical Trials
- Participating in clinical trials offers access to innovative treatments and contributes to advancements in PsA research. Clinical trial participation may be beneficial for individuals seeking alternative treatment options or those with refractory PsA symptoms.
Takeaway
Psoriatic arthritis is a complex condition requiring a personalized treatment approach tailored to individual needs and preferences. By collaborating with healthcare providers and exploring diverse treatment modalities, individuals with moderate to severe PsA can effectively manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and reduce the risk of long-term joint damage. If you have PsA, consult with your healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses your unique concerns and goals.
Arthritis treatment focuses on dietary adjustments, natural remedies, and lifestyle modifications. Alkaline diets rich in fruits and vegetables, along with raw vegetable juice therapy, are recommended. Bromelain in fresh pineapple juice and raw potato juice are beneficial for reducing inflammation.
Home Remedies
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) often requires a holistic approach to management, encompassing both conventional treatments and complementary or alternative therapies. While these therapies may not replace traditional medical interventions, they can complement them, providing additional relief and improving overall well-being. Let’s explore some of the complementary and alternative therapies commonly used for PsA:
- Acupuncture: This ancient practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to alleviate pain and promote healing. While research specific to PsA is limited, acupuncture may offer relief for some individuals by stimulating the body’s natural pain-relieving mechanisms.
- Massage: Manipulating soft tissues through massage therapy can help reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and alleviate pain associated with PsA. Although evidence supporting its efficacy for PsA is lacking, many people find massage beneficial for managing symptoms and promoting relaxation.
- Curcumin: Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, possesses potent anti-inflammatory properties that may help ease joint pain and inflammation in PsA. While further research is needed to confirm its effectiveness, some individuals find relief from incorporating curcumin supplements into their treatment regimen.
- Vitamin D: Adequate vitamin D levels are essential for maintaining overall health and supporting immune function. Research suggests that vitamin D deficiency may be linked to autoimmune conditions like PsA. Supplementing with vitamin D or increasing sun exposure under medical supervision may help alleviate symptoms and improve outcomes.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: Mind-body practices like yoga and tai chi combine gentle movements, breathing techniques, and meditation to enhance flexibility, reduce stress, and promote relaxation. Both yoga and tai chi can improve joint mobility, muscle strength, and overall well-being in individuals with PsA.
- Reiki: Reiki is a form of energy healing that aims to balance the body’s energy flow and promote self-healing. While scientific evidence supporting its efficacy is limited, some individuals report feeling more relaxed and less stressed after undergoing Reiki sessions.
Lifestyle Changes for Psoriatic Arthritis Management
In addition to complementary and alternative therapies, certain lifestyle modifications can play a crucial role in managing PsA and improving quality of life:
- Joint Protection: Applying heat or cold treatments, avoiding overexertion, and practicing proper body mechanics can help protect joints and alleviate pain.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants can support overall health and reduce inflammation in PsA.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and walking can improve joint flexibility, muscle strength, and cardiovascular health. Consult with a healthcare provider or physical therapist to develop an exercise program tailored to your needs.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is essential for individuals with PsA, as smoking can worsen symptoms and interfere with treatment effectiveness.
Participation in Clinical Trials
Clinical trials play a vital role in advancing our understanding of PsA and developing new treatment options. By participating in clinical trials, individuals with PsA can access cutting-edge therapies and contribute to the advancement of medical science.
In conclusion, while PsA presents unique challenges, a comprehensive treatment approach that includes complementary and alternative therapies, lifestyle modifications, and participation in clinical trials can help individuals manage symptoms, improve function, and enhance overall well-being. If you have PsA, consult with your healthcare provider to explore all available treatment options and develop a personalized management plan tailored to your needs and preferences.
Various home remedies can alleviate arthritis symptoms. Black gingelly seeds, soaked in water overnight, and copper-infused water are effective in relieving joint pain. Warm oil massages with camphor and herbal remedies like green-gram soup and fenugreek seeds also provide relief.
Yoga and Exercise
Yoga for Psoriatic Arthritis: Does It Help or Hurt?
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a challenging condition characterized by swollen joints, stiffness, and pain, which can significantly impact mobility and quality of life. While there’s no cure for PsA, incorporating regular exercise into your routine can effectively manage symptoms and enhance well-being. One such exercise modality gaining attention for its potential benefits is yoga. Let’s delve into the world of yoga for Psoriatic Arthritis: its poses, types, benefits, precautions, and key takeaways.
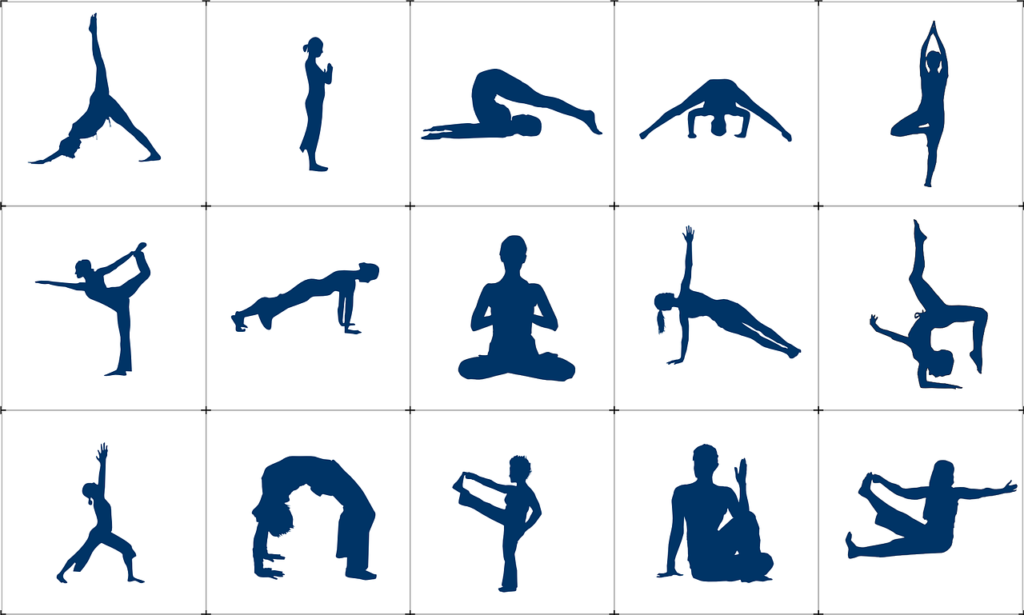

Yoga for Psoriatic Arthritis
Yoga presents a gentle, low-impact approach to building strength, flexibility, and balance, all without placing undue stress on the joints. Importantly, it’s adaptable to individual needs, making it suitable for varying fitness levels and abilities. However, it’s crucial to practice mindfulness during yoga sessions, avoiding poses or movements that may exacerbate PsA symptoms.
Yoga Poses for Psoriatic Arthritis
- Seated Spinal Twist: Enhances spinal flexibility and mobility.
- Bridge: Strengthens the lower back and glutes while stretching the chest and neck.
- Cat-Cow: Promotes spinal flexibility and relieves tension.
- Cobbler’s Pose: Stretches the inner thighs and groin muscles.
- Standing Forward Fold: Relieves tension in the hamstrings and lower back.
- Warrior II: Builds strength in the legs and core while improving balance.
- Baby Cobra: Strengthens the back muscles and improves posture.
Types of Yoga
Yoga encompasses various styles, each offering unique benefits. Some of the most popular types include Bikram, Anusara, Viniyoga, Kripalu, Iyengar, and Ashtanga. When choosing a yoga style for PsA, focus on those emphasizing proper alignment, controlled movements, and breath awareness.
Benefits of Yoga for Psoriatic Arthritis
While scientific evidence specific to PsA is limited, regular yoga practice has been associated with numerous physical and emotional benefits. These include pain relief, increased flexibility, enhanced balance, improved blood circulation, stress reduction, and enhanced emotional well-being.
Precautions
Before embarking on a yoga journey, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider, especially if you have PsA. Additionally, listen to your body during practice, avoiding poses that cause discomfort or strain. Opt for gentle, modified movements, and be cautious with poses requiring excessive joint bending or balancing.
Takeaway
In conclusion, yoga can be a valuable addition to the management plan for Psoriatic Arthritis. Its gentle nature, adaptability, and holistic benefits make it an attractive option for individuals seeking relief from PsA symptoms. However, always prioritize safety and consult with your healthcare provider before initiating any new exercise regimen. With mindfulness and proper guidance, yoga can be a powerful tool in enhancing overall well-being and managing PsA effectively.
Yoga asanas such as trikonasana and bhujangasana, along with pranayama techniques, help improve flexibility and reduce arthritis symptoms. Light exercises like walking and swimming are beneficial for joint mobility and overall health.
Other Therapies
Supplements
- Turmeric (Curcumin): Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, curcumin supplements may help ease arthritis symptoms.
- Fish Oil: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fish oil supplements can reduce joint tenderness and stiffness.
- Vitamin D: Addressing vitamin D deficiency, either through supplements or sunlight exposure, supports bone health.
- Ginger: Although not specifically studied for PsA, ginger’s anti-inflammatory properties may offer relief from pain and inflammation.
Topical Therapies
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Alternating between warm soaks and cold packs can soothe achy joints and reduce swelling.
- Epsom Salts: Soaking in an Epsom salt bath may alleviate joint pain and inflammation.
- Dead Sea Salts: Balneotherapy with Dead Sea salts has shown promise in reducing inflammation and improving skin symptoms.
- Capsaicin: Found in spicy peppers, capsaicin creams or patches provide a numbing effect on pain receptors.
Bodywork
- Massage: Professional massage therapy can relieve muscle tension and improve joint mobility.
- Acupuncture: Traditional Chinese medicine involving the insertion of needles into specific points on the body may offer pain relief and relaxation.
- Acupressure: Applying pressure to specific points on the body without needles can release tension and reduce pain.
Stress Relief
- Meditation: Mindfulness meditation techniques can reduce stress levels and enhance overall well-being.
- Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate activities like yoga, reading, or listening to music to unwind and alleviate stress.
Overall Well-Being
- Diet: Focus on an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, healthy fats, and lean proteins to support joint health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, including low-impact exercises like swimming and yoga, improves joint flexibility and reduces fatigue.
- Sleep Hygiene: Prioritize quality sleep by maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking can reduce PsA symptoms and decrease the risk of disease progression.
Takeaway
While natural treatments can complement conventional therapies for Psoriatic Arthritis, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating any new remedies into your regimen. By taking a holistic approach to PsA management, individuals can effectively alleviate symptoms, improve joint function, and enhance overall quality of life.
Hydrotherapy, massage, and acupuncture offer additional benefits for arthritis patients. Hot foot baths, steam baths, and exposure to infra-red rays help reduce inflammation and stiffness. Alternative treatments complement conventional therapies for arthritis management.
Conclusion
Arthritis is a debilitating condition that affects millions worldwide. By adopting a holistic approach to treatment, including diet, natural remedies, and exercise, individuals can manage symptoms and improve their quality of life.

FAQS
- What is arthritis?
- Arthritis is a chronic disease characterized by joint inflammation and pain.
- What are the different types of arthritis?
- The main types of arthritis include osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
- What are the common symptoms of arthritis?
- Symptoms of arthritis include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and deformity.
- How can arthritis be treated?
- Treatment options include dietary changes, natural remedies, exercise, and therapies like massage and acupuncture.
- Are there any natural remedies for arthritis?
- Yes, natural remedies such as raw vegetable juice therapy, pineapple juice, and warm oil massages can help alleviate arthritis symptoms.
