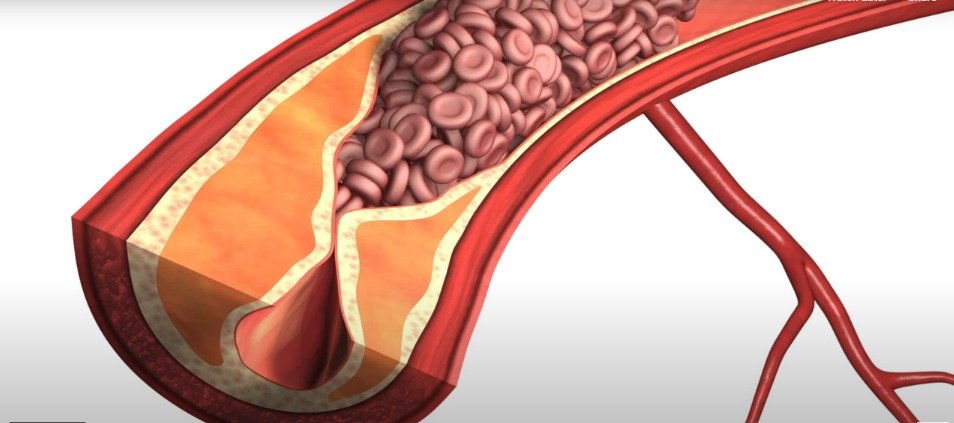
Introduction to Arteriosclerosis
Atherosclerosis, often referred to as hardening of the arteries, is a prevalent condition characterized by the narrowing of arteries due to plaque buildup. This buildup restricts blood flow, leading to various complications, including heart attack and stroke. Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding atherosclerosis:
Causes of Arteriosclerosis
- High Cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels contribute to plaque formation in arteries.
- Unhealthy Diet: Consuming foods high in saturated fats and cholesterol accelerates plaque buildup.
- Aging: Arteries naturally become less elastic with age, increasing susceptibility to plaque accumulation.
Arteriosclerosis is primarily caused by dietary habits, sedentary lifestyle, genetic factors, and other underlying health conditions. Excessive intake of white sugar, refined foods, and high-fat diets rich in cholesterol contributes to the development of arteriosclerosis. Sedentary habits and emotional stress also play significant roles in its onset.
Symptoms of Arteriosclerosis
- Mostly Silent: Atherosclerosis often remains asymptomatic until a blockage occurs.
- Common Indications: Symptoms may include chest pain, leg cramping, shortness of breath, fatigue, and confusion.
- Emergency Signs: Recognize symptoms of heart attack (chest pain, sweating) and stroke (weakness, trouble speaking) for immediate medical attention.
The symptoms of arteriosclerosis vary depending on the arteries involved. Common signs include numbness, coldness, cramps, and pain in the legs, particularly after exercise. Involvement of coronary arteries may lead to angina pectoris, while blockage of arteries to the brain can result in strokes or transient ischemic attacks. High blood pressure and kidney disorders may also occur if arteries leading to the kidneys are affected.
Diagnosis
- Physical Exam: Doctors assess pulse strength, check for aneurysms, and listen for abnormal sounds.
- Diagnostic Tests: Blood tests, ultrasounds, angiograms, and EKGs help detect atherosclerosis and assess its severity.
Treatment
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing stress are crucial.
- Medications: Cholesterol-lowering drugs, blood pressure medications, and antiplatelet drugs may be prescribed.
- Surgical Procedures: In severe cases, bypass surgery, angioplasty, or endarterectomy may be necessary.
Risk Factors
- Family History: Genetics play a role in predisposing individuals to atherosclerosis.
- Lack of Exercise: Sedentary lifestyles increase the risk of arterial plaque buildup.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension weakens arteries, making them more prone to plaque formation.
- Smoking: Tobacco use damages blood vessels and accelerates atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes have a higher risk of developing atherosclerosis-related complications.
Complications
- Heart Disease: Atherosclerosis can lead to heart failure, abnormal heart rhythms, and coronary artery disease.
- Stroke: Reduced blood flow to the brain increases the risk of stroke.
- Peripheral Artery Disease: Impaired circulation in the limbs can result in pain and tissue damage.
- Kidney Disease: Atherosclerosis affecting renal arteries may lead to kidney failure.
Prevention
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintain a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, and avoid tobacco use.
- Medical Management: Control blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and diabetes with medication if necessary.
- Weight Management: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on the cardiovascular system.
Outlook
- Long-Term Management: Atherosclerosis is a chronic condition that requires lifelong management.
- Treatment Efficacy: Success depends on the severity of the condition, timely intervention, and adherence to treatment.
- Lifestyle Impact: Making healthy lifestyle changes can slow down disease progression and reduce the risk of complications.
Treatment Approaches for Arteriosclerosis
Treatment of arteriosclerosis focuses on addressing underlying causes and promoting vascular health. Patients may undergo short juice fasts followed by a balanced diet rich in seeds, nuts, grains, vegetables, and fruits. Dietary modifications, including the avoidance of refined and processed foods, saturated fats, and excess salt, are essential. Natural remedies such as garlic, onions, lemon peel, parsley, and beet juice have shown beneficial effects in managing arteriosclerosis.
Preventive Measures
Preventing arteriosclerosis involves adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, stress management, and a balanced diet. Emphasis should be placed on consuming raw foods, avoiding smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight. Home remedies such as lemon peel, parsley, and beet juice can also be incorporated into daily routines to promote vascular health.
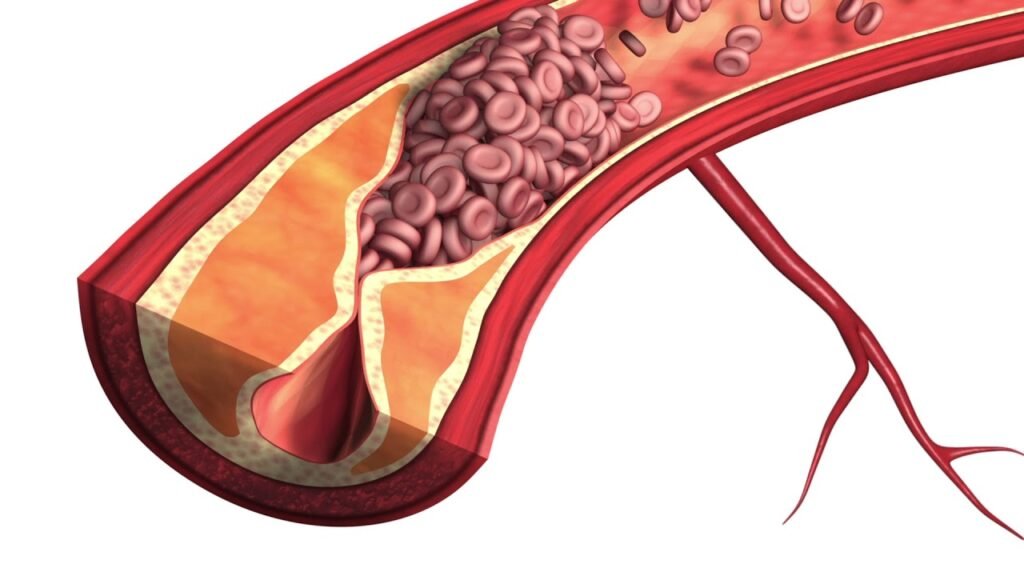
Crackdown on Atherosclerosis: Understanding, Treatment, and Prevention
Hey there, health enthusiasts! Today, let’s delve into the nitty-gritty of atherosclerosis – the sneaky condition that messes with your arteries. But fear not! We’re here to break it down, from what it is to how to tackle it head-on.
What’s the Deal with Atherosclerosis?
So, what exactly is atherosclerosis? Well, it’s like a slow-motion traffic jam in your arteries, caused by a buildup of plaque. Picture this: your arteries are the highways, carrying oxygen and nutrients throughout your body. But when plaque sticks to their walls, it’s like throwing a giant roadblock in the way.
Can You Reverse Atherosclerosis?
Now, onto the million-dollar question: can you hit reverse on atherosclerosis? Dr. Howard Weintraub says not quite. Once it’s there, the best we can do is slow its roll and prevent complications. But fear not – we’ve got some tricks up our sleeves.
Battling Atherosclerosis: Treatment and Lifestyle Changes
First up, meds. Statins are the heroes here, slashing cholesterol levels and keeping plaque in check. But they’re not the only players. Lifestyle changes are crucial too. Think heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and kicking those smoking habits to the curb.
Tips for a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Let’s talk diet. Ditch the sugary drinks and load up on fiber-rich fruits and veggies. Healthy fats like olive oil and nuts? Yes, please! And when it comes to meat, lean cuts are the way to go. Oh, and don’t forget to watch that sodium intake – your heart will thank you.
When Meds Aren’t Cutting It: Surgery to the Rescue
Now, what if all else fails? Surgery might be the next step. Surgeons can swoop in and clear out plaque or even reroute blood flow if things get hairy. It’s like a highway cleanup crew, but for your arteries.
Getting to the Heart of the Matter: Diagnosis
But how do you know if atherosclerosis is lurking in your arteries? Well, your doc might spot some red flags during a checkup. And if they suspect trouble, they’ll order some tests, like ultrasounds or stress tests, to get the full picture.
Takeaway: Beating Atherosclerosis
So, here’s the bottom line: atherosclerosis might be a tough nut to crack, but with the right tools – meds, lifestyle changes, and maybe a little surgery – you can keep it in check. Just remember to chat with your doc about the best plan of attack for you.
Conclusion
In conclusion, arteriosclerosis is a common vascular disease that can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent and manage arteriosclerosis, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular events.

FAQS
- What is arteriosclerosis?
- Arteriosclerosis refers to the thickening of artery walls due to the accumulation of calcium or lime, leading to impaired blood circulation.
- What are the common causes of arteriosclerosis?
- Arteriosclerosis is primarily caused by dietary habits, sedentary lifestyle, genetic factors, and other underlying health conditions.
- What are the symptoms of arteriosclerosis?
- Symptoms include numbness, coldness, cramps, and pain in the legs, angina pectoris, strokes, transient ischemic attacks, high blood pressure, and kidney disorders.
- How is arteriosclerosis treated?
- Treatment involves dietary modifications, fasting, natural remedies, lifestyle changes, and stress management to promote vascular health.
- Are there any preventive measures for arteriosclerosis?
- Yes, preventive measures include adopting a healthy lifestyle, regular exercise, stress management, and dietary modifications to maintain vascular health.